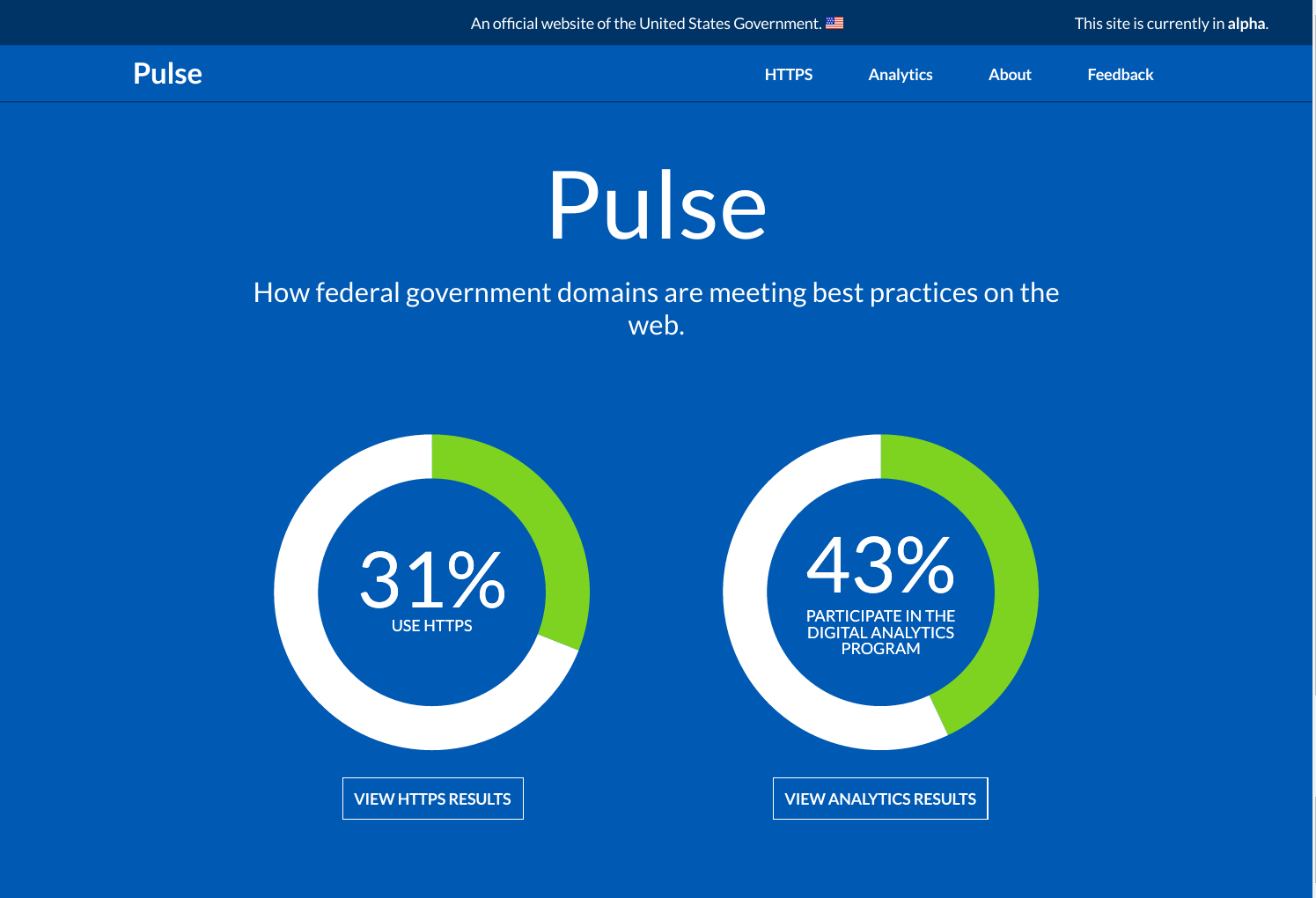
The U.S. federal government is launching a new project to monitor how it's doing at best practices on the web.
A sort of health monitor for the U.S. government's websites, it's called Pulse, and you can find it at pulse.cio.gov.
Pulse is a lightweight dashboard that uses the official .gov domain list to measure two things:
- Analytics: Whether federal executive branch domains are participating in the Digital Analytics Program that powers analytics.usa.gov.
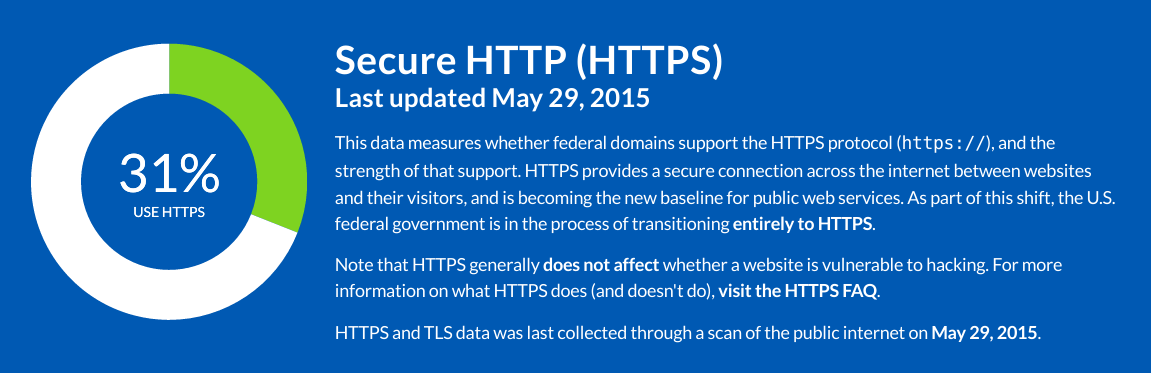
- HTTPS: Whether federal domains have deployed the HTTPS protocol, and how well they've done it.
These two things are just a start — there are a lot of other important things worth measuring! It's also important to note that Pulse is currently only measuring parent domains (e.g. agency.gov) and is not measuring subdomains (e.g. portal.agency.gov).
The project will hopefully expand over time to measure more best practices and more websites. In the meantime, Pulse is a commitment by the U.S. government to build a world-class analytics program and to transition entirely to HTTPS.
Background
Pulse is a collaboration between 18F and the Office of Government-wide Policy (OGP).
Like 18F, OGP is an office of the U.S. General Services Administration. Among many other things, OGP operates the .gov domain registry and the CIO Council, an interagency forum of Chief Information Officers.
18F previously partnered with OGP in December to release the complete .gov domain list. Since then, 18F has worked with the Digital Analytics Program to build analytics.usa.gov, and has coordinated with a number of agencies to strengthen HTTPS for federal .gov domains. We're deeply gratified that we've had the opportunity to work with OGP to create a platform that continues this momentum.
How pulse.cio.gov works
Pulse was created in around six weeks. We built the project in the open from Day 1, obtained our domain name and relevant cybersecurity approvals in our first couple weeks, and released new versions of the dashboard to pulse.cio.gov early and often throughout the process.
We also gathered usability feedback throughout development from users both inside and outside of the government, and repeatedly incorporated the results of that feedback into our work. Even though Pulse is only a handful of pages and puts most of its data into a simple table, we wanted to pay attention to detail and take the same user-centered approach 18F takes with our larger projects.
Pulse is a static website whose data is created from a combination of sources:
- The official .gov domain list. This is currently exported manually by GSA staff on a roughly quarterly basis.
- The list of websites which participate in the Digital Analytics Program. This is also currently exported manually by GSA staff on a roughly quarterly basis.
- Data collected from a public scan of how federal domains respond to HTTP and HTTPS, using an open source tool by Ben Balter called
site-inspector. - Data collected from a public scan of HTTPS configuration details for federal domains, using the SSL Labs API.
To coordinate the data collection process, we created domain-scan, a small Python command line tool that runs domains through site-inspector and the SSL Labs API and produces CSV reports.
We then run these CSVs through a final step, where we take the low-level primitives we gathered during the scanning process and create some higher-level conclusions and save them in a format that Pulse can automatically render into a table.
The process is not fully automated, and so Pulse isn't updated every day. There's work to do on all of the above to get to the point of showing fully up-to-date data without human intervention.
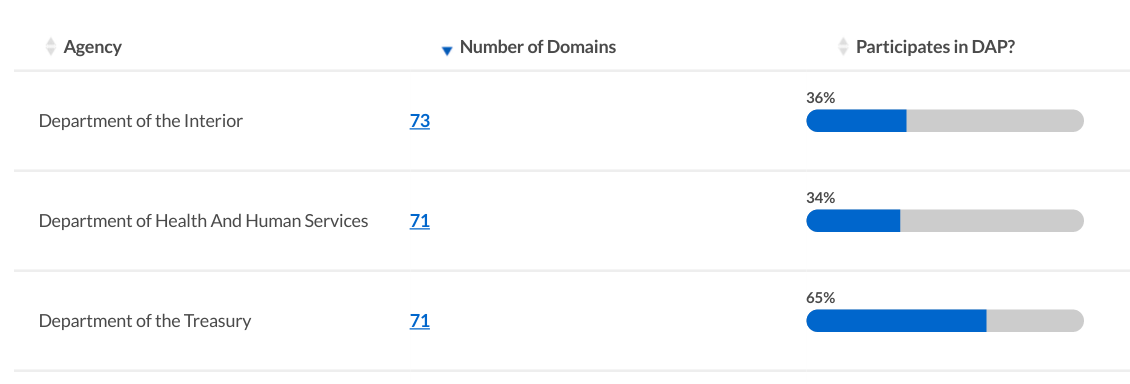
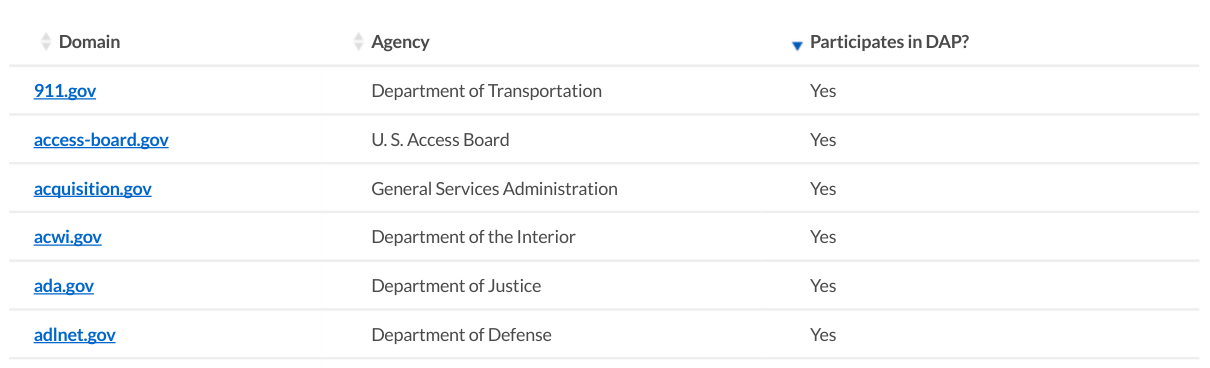
Measuring participation in the Digital Analytics Program
The Digital Analytics Program is a free, shared web analytics service for U.S. federal agencies.
To participate, agencies place some JavaScript on their websites that report to a combined analytics account. The Digital Analytics Program has privacy controls that anonymize visitor addresses and restrict data sharing.
Access to the account is shared within the federal government, and much of its data is shared publicly on analytics.usa.gov. The Digital Analytics Program also regularly publishes a list of around 4,000 participating websites that have reported visitor data in the preceding 2 weeks.
Pulse measures participation in the simplest way possible: by comparing the .gov domain list to the list of participating websites published by the Digital Analytics Program. It's not rocket science, but in the future we'd like to automate this process using the analytics-reporter tool we created for analytics.usa.gov.
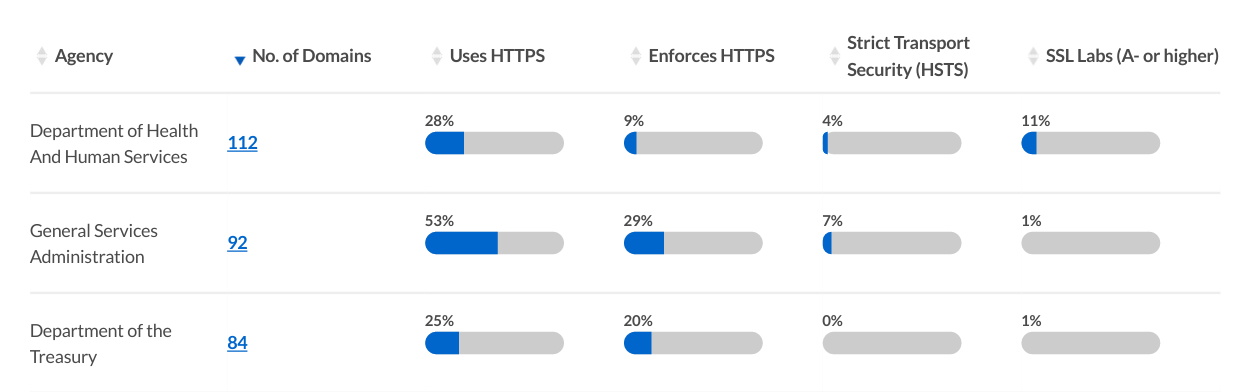
Measuring HTTPS in .gov
Enforcing strong HTTPS is an important baseline for government websites, and is in the process of becoming the baseline for the web at large.
HTTPS is simple enough to detect, but characterizing HTTPS support for a domain, precisely and reliably, is trickier than you might expect.
We lean heavily on the open source site-inspector, a command line tool written in Ruby. site-inspector measures various useful things about websites, and was originally written by Ben Balter to analyze .gov domains.
To get the precision we wanted, we needed to take into account several subtle things about domains:
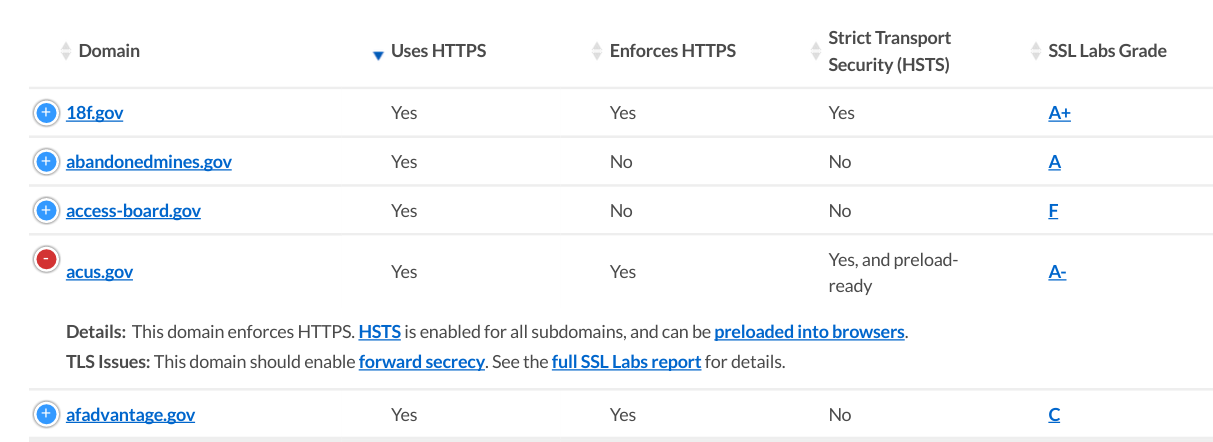
- Domains have 4 possible "endpoints" —
https://www,https://,http://www, andhttp://— which may each exhibit very different behavior. Describing a domain's HTTPS support means detecting which endpoint is "canonical," as well as looking holistically at which endpoints redirect to others. - A domain's HTTPS certificate might be issued for an invalid hostname (e.g.
a248.e.akamai.net). In this case, HTTPS is likely an unsupported way to access the domain. - A domain's HTTPS certificate might have an incomplete or untrusted chain (e.g. missing intermediates, or a private root certificate), in which case HTTPS is likely a supported way to access the domain.
- A domain might set an HSTS policy for
www, but neglect to apply one to the bare domain, negating HSTS policy for its other subdomains. - A domain might support HTTPS with a valid certificate, but have a policy of "downgrading" users by redirecting away from HTTPS to HTTP.
We use site-inspector to look at all of the above factors (and many more) and calculate a bunch of helpful things about a domain's HTTPS support. If you really want to dive deeply into the methodology, you can read the original work discussion.
To measure HTTPS quality, we lean on SSL Labs. SSL Labs' grading system has become a widely respected, universally referenced gauge of HTTPS quality. (Here's the report for Pulse itself.)
We used ssllabs-scan, an open source client for the SSL Labs API, to collect the top-level grade along with some common relevant issues that are worth addressing (such as forward secrecy, or the use of SHA-1 signatures).
Looking forward
We're still in the process of fully documenting the tools we used. If you're interested in using any of it in your own work, and you have questions about how to get started, ring in on GitHub. We're an open source team, and we'd love your contributions!
Pulse is clearly a small and simple website, but we think it's a promising foundation for celebrating (and motivating) the U.S. government's progress on making world-class websites and online services.
We're thrilled we had the opportunity to work with the Office of Government-wide Policy here at GSA to get Pulse started, and we hope others find it useful. Feel free to leave feedback on the project so far, and where to take Pulse next!